A social incentive such as a personalised table of questionnaire response to date to evidence previous responses noted and valued are included in the cover letter.
Including a social incentive in the cover letter may result in little or no difference to retention.
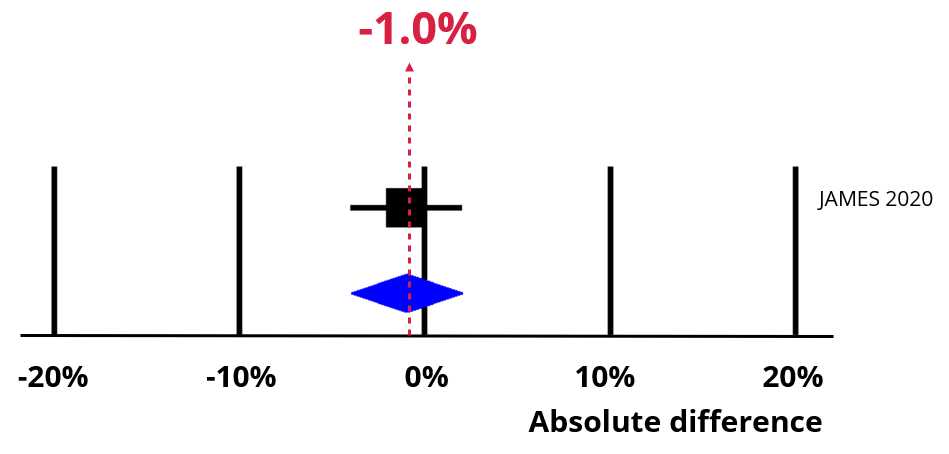
An increase of -1% (95% confidence interval = -4% to 2%).
GRADE Low certainty.
We recommend that trialists include a social incentive in cover letters in the context of an intervention evaluation.
See Resource bundle below for details on how to use social incentives.
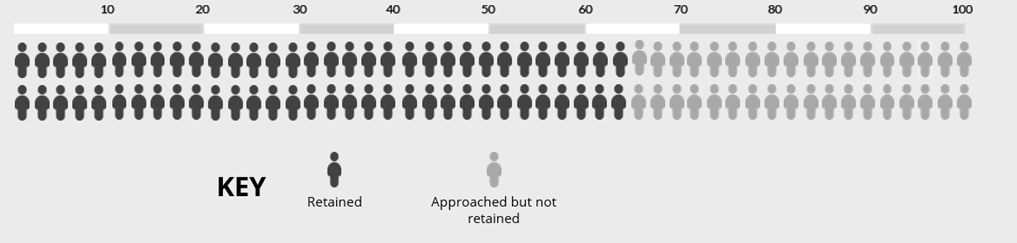
Imagine initial retention is 65% of those approached. You have a trial with 100 participants that needs responses from 80 to meet its statistical power calculations. Retention of 65% means that you will be 15 responses short (see chart below).

Now imagine using a social incentive. The chart below shows the impact of an absolute increase of -1% (95% CI = -4% to 2%). Retention is now 64%, which means our best estimate is that you would now be 14 responses short.